
Dubai Building Codes: Essential Regulations for Your Project
Building in Dubai: A Comprehensive Guide to Essential Regulations
This guide provides eight essential Dubai building codes for construction professionals in the UAE. Understanding these regulations is crucial for project success, ensuring compliance with Dubai's standards for safety, sustainability, and accessibility. From structural requirements and fire safety to green building practices and seismic design, this list covers key aspects of the Dubai Building Code (DBC) and other relevant regulations. Whether you're building a new structure or renovating an existing one, adhering to these codes is essential for operating in Dubai. Let Yasu Trading Co. LLC support your project needs throughout the construction process.
1. Dubai Building Code (DBC) - Structural Safety Requirements
The Dubai Building Code (DBC) forms the backbone of structural safety for all construction projects within the Emirate. It establishes comprehensive standards, mandating specific load-bearing calculations, seismic resistance measures, and material specifications. These stringent regulations are crucial for ensuring building integrity and resilience against the region's unique climatic and geological conditions, including extreme heat, occasional seismic activity, and specific soil characteristics. The DBC plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public safety, minimizing long-term maintenance issues, and boosting property values by assuring quality construction. This makes it an essential consideration for anyone involved in the construction and maintenance of buildings in Dubai, from individual homeowners to large-scale developers.

The DBC's structural safety requirements are not merely a checklist, but a deeply integrated system. It dictates how structural engineers must approach design, ensuring calculations accurately reflect the anticipated loads and stresses a building will experience. This involves analyzing factors like dead loads (the weight of the building itself), live loads (occupants, furniture, etc.), wind loads (especially crucial for high-rise structures prevalent in Dubai), and seismic loads.
Specific features of the DBC's structural component include:
- Mandatory seismic design requirements: Buildings over three stories must be designed to withstand seismic activity, a crucial safety measure given the region's proximity to fault lines.
- Wind load calculations: For buildings exceeding 50 meters in height, rigorous wind load calculations are mandatory, factoring in the potential impact of strong winds and sandstorms common in the UAE.
- Concrete and Steel specifications: The DBC specifies minimum concrete strength (e.g., 25 MPa for residential buildings) and dictates steel reinforcement specifications suitable for high-temperature environments, addressing the challenges posed by Dubai’s climate.
- Foundation depth requirements: Soil analysis is mandatory to determine the appropriate foundation depth, ensuring stability and preventing settlement issues related to the varied soil conditions across Dubai.
The DBC brings significant benefits to the construction landscape in Dubai:
- Enhanced public safety: Rigorous structural standards protect occupants and the public, minimizing the risk of structural failures.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Durable and well-designed structures lead to lower long-term maintenance costs, a significant advantage for building owners and facility managers.
- Increased property values: Compliance with the DBC provides quality assurance, enhancing property values and investor confidence.
- International recognition and compliance: Adherence to international best practices enhances Dubai's reputation for construction excellence.
However, complying with the DBC also presents certain challenges:
- Higher initial construction costs: Implementing advanced structural designs and high-quality materials can increase upfront construction expenses.
- Extended approval processes: Meeting the stringent requirements necessitates detailed documentation and thorough reviews, potentially extending project timelines.
- Complex documentation requirements: Navigating the complex regulations requires meticulous documentation, demanding specialized expertise and resources.
- Need for specialized engineering expertise: Successful DBC compliance necessitates engaging qualified structural engineers with in-depth knowledge of UAE-specific conditions.
Iconic structures like the Burj Khalifa, with its advanced structural design incorporating DBC requirements, exemplify the code's successful implementation. Similarly, the wind resistance measures implemented in Dubai Marina towers and the integrated structural compliance showcased in the Al Habtoor City development underscore the DBC's practical application and impact.
For those involved in construction projects in Dubai, adherence to the DBC is not optional but essential. Here are some actionable tips to ensure smooth compliance:
- Engage early: Bring in structural engineers familiar with UAE conditions early in the design phase. Their expertise will be invaluable in navigating the DBC requirements and optimizing structural design.
- Thorough soil testing: Conduct comprehensive soil testing before finalizing foundation designs. This is critical for determining appropriate foundation depth and ensuring long-term stability.
- Certified materials: Use only certified materials that meet DBC specifications. This ensures the structural integrity and durability of the building.
- Regular inspections: Plan for regular structural inspections during the construction process. This helps identify and address potential issues early on, preventing costly rectifications later.
For those looking to understand more about the intricacies of building inspections and compliance, you can Learn more about Dubai Building Code (DBC) - Structural Safety Requirements. Ultimately, understanding and adhering to the Dubai Building Code is paramount for ensuring safe, durable, and valuable buildings in the dynamic landscape of Dubai. By adhering to these standards, construction professionals contribute to a safer and more resilient built environment for all.
2. Fire Safety and Life Protection Code
Fire safety is paramount in any building project, and Dubai's stringent building codes reflect this priority. The Fire Safety and Life Protection Code within the Dubai building codes mandates advanced fire prevention, detection, and suppression systems in all constructions, ensuring the highest level of safety for occupants and safeguarding property investments. These regulations are not static; they adapt based on the building type, occupancy load, and height, recognizing the unique fire safety challenges presented by different structures. This comprehensive approach minimizes fire risks and promotes a culture of safety within the Emirate.

The code operates on a multi-layered approach, covering everything from initial design and construction to ongoing maintenance and emergency preparedness. It dictates the use of fire-resistant materials in construction, mandates the installation of sophisticated fire detection and alarm systems, and outlines specific requirements for firefighting equipment and access. The code also emphasizes the importance of well-defined emergency evacuation plans, clearly marked exit routes, and regular fire drills to ensure occupants can swiftly and safely evacuate in case of a fire.
For buildings over 18 meters tall, the code mandates the installation of sprinkler systems, a proven technology for suppressing fires in their early stages. This requirement, while potentially adding to the initial construction cost, significantly reduces the risk of large-scale fire damage and potential casualties. The code also addresses fire compartmentalization, requiring the division of larger buildings into smaller, fire-resistant compartments to limit the spread of fire and smoke.
Several prominent buildings in Dubai exemplify the successful implementation of the Fire Safety and Life Protection Code. The Dubai Mall, with its high occupancy and complex layout, boasts a comprehensive fire safety system featuring advanced suppression technology. Similarly, the Emirates Towers’ integrated fire safety design showcases the code’s emphasis on incorporating safety measures from the earliest stages of a project. Dubai International Airport, with its specialized aviation fire protection systems, demonstrates the code's adaptability to specific industry needs.
Pros of Adhering to the Fire Safety and Life Protection Code:
- Significantly reduced fire casualties and property damage: The proactive approach minimizes the risk of fire incidents and limits their impact.
- Lower insurance premiums for compliant buildings: Insurers recognize the reduced risk associated with code-compliant buildings, often resulting in lower premiums.
- Enhanced emergency response capabilities: The code facilitates a swift and effective response from emergency services.
- International safety standard compliance: Dubai's fire safety regulations align with international best practices, assuring stakeholders of a high level of safety.
Cons of Implementing the Code:
- Substantial initial investment in fire safety systems: Implementing advanced fire safety systems can represent a significant upfront cost.
- Ongoing maintenance and testing costs: Regular maintenance and testing of fire safety equipment are essential for optimal performance, incurring ongoing expenses.
- Design constraints to accommodate safety features: Integrating fire safety features can sometimes impose limitations on building design and aesthetics.
- Regular training requirements for building management: Building management personnel must undergo regular training to ensure they are equipped to handle fire emergencies effectively.
Actionable Tips for Compliance with the Fire Safety and Life Protection Code:
- Install fire safety systems during initial construction: Integrating these systems during construction is often more cost-effective than retrofitting later.
- Conduct regular fire drills and staff training: Regular drills familiarize occupants with evacuation procedures and ensure a swift and organized response in a real emergency.
- Maintain detailed fire safety documentation: Meticulous record-keeping demonstrates compliance and aids in ongoing maintenance and inspections.
- Use certified fire safety contractors and equipment: Engaging certified professionals guarantees the quality and reliability of fire safety systems.
The Fire Safety and Life Protection Code is a cornerstone of Dubai's building codes for good reason. It prioritizes life safety, minimizes property damage, and promotes a culture of fire safety awareness. For construction companies, developers, and building managers operating in Dubai, adhering to this code is not just a legal requirement, it's a crucial investment in the safety and well-being of occupants and the long-term value of their properties. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term benefits, in terms of reduced risk, lower insurance premiums, and enhanced safety, far outweigh the costs. By prioritizing fire safety, stakeholders contribute to creating a safer and more resilient built environment in Dubai.
3. Energy Efficiency and Green Building Standards
Dubai's rapid development has brought with it a growing awareness of the importance of sustainable practices. Integrated into the very fabric of Dubai's building codes are stringent energy efficiency and green building standards. These regulations are not merely suggestions but crucial components of the emirate's ambitious vision for sustainable development, including achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. These standards reflect a commitment to responsible growth, ensuring that Dubai's iconic skyline also represents a responsible approach to environmental stewardship. They play a pivotal role in shaping a future where buildings contribute positively to the environment and enhance the quality of life for residents. These regulations are essential for any project in Dubai, driving the construction industry towards a greener future.

These green building regulations promote sustainable construction by mandating energy efficiency requirements, encouraging renewable energy integration, and implementing environmental impact reduction measures. They provide a framework for constructing buildings that consume fewer resources, generate less waste, and minimize their overall environmental footprint. This approach aligns perfectly with the UAE's broader vision of sustainable development, demonstrating Dubai's commitment to global environmental responsibility.
Specifically, Dubai's building codes require a minimum of 20% energy savings compared to baseline buildings, a significant reduction that impacts operational costs over the long term. Solar panel installations are increasingly required for new developments, harnessing the abundant sunlight in the region to generate clean energy. The codes also address efficient HVAC systems with smart controls, recognizing the significant energy consumption associated with climate control in a desert environment. Furthermore, green roof and landscaping mandates not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also contribute to improved insulation and reduced urban heat island effect. Finally, water conservation and recycling systems are integral to addressing water scarcity, a critical concern in the region.
The benefits of adhering to these standards are multifaceted. Reduced operational costs due to energy savings are a significant driver for developers and building owners. Moreover, incorporating green building features enhances property marketability and value, attracting environmentally conscious tenants and investors. Compliance with these regulations naturally contributes to environmental impact reduction, aligning with global sustainability goals. Finally, meeting these local standards often aligns with achieving recognition from international sustainability standards such as LEED and BREEAM, further enhancing a project's prestige.
However, implementing these green building features is not without its challenges. Higher upfront construction costs can be a barrier, particularly for smaller projects. The technical complexity in design and implementation requires specialized expertise, which can add to project timelines and budgets. Limited availability of certified green materials in the region can also present logistical hurdles. Finally, the need for specialized expertise and certifications necessitates engaging qualified professionals who understand the nuances of green building design and implementation.
Despite these challenges, the successful implementation of these standards is evident across Dubai. The Sustainable City Dubai, for example, has achieved net-zero energy consumption, showcasing the potential of integrated sustainable design. The Dubai International Financial Centre boasts numerous LEED-certified buildings, demonstrating the commitment of prominent developments to green building practices. Al Shera'a development further exemplifies the incorporation of comprehensive green building features. You can learn more about Energy Efficiency and Green Building Standards and explore successful implementations of eco-friendly materials.
For those involved in construction projects in Dubai, adhering to these standards is crucial for long-term success. Engaging LEED or BREEAM certified consultants early in the design phase can optimize the integration of green building features. Prioritizing passive design strategies, such as building orientation and natural ventilation, can significantly reduce energy consumption. Selecting locally available sustainable materials, when possible, minimizes transportation costs and environmental impact. Implementing building management systems for ongoing energy monitoring ensures continued efficiency and allows for adjustments as needed. By embracing these best practices, construction professionals can contribute to Dubai's vision of a sustainable future while reaping the numerous benefits of green building.
4. Accessibility and Universal Design Requirements
Accessibility is not just a buzzword in Dubai's building codes; it's a fundamental principle shaping the city's inclusive urban development. Dubai's commitment to creating a barrier-free environment is reflected in its comprehensive accessibility requirements, ensuring that all buildings, from residential complexes to public spaces, cater to the needs of people with disabilities and mobility challenges. This commitment benefits everyone, fostering a truly inclusive society. This aspect of Dubai building codes is crucial not just for legal compliance, but also for ethical reasons and long-term social benefit. These requirements affect numerous professionals within the AE region, including construction companies, architects, facility managers, and real estate developers, making a thorough understanding vital for project success.
Dubai's accessibility code goes beyond simply ticking boxes. It encompasses a detailed set of design standards that influence every aspect of a building's layout, from entrances and circulation paths to facilities and emergency egress. These standards are rooted in the understanding that accessibility is not an afterthought but an integral part of good design. This approach aligns with the broader goal of universal design, which aims to create environments usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design.
Key Features of Dubai's Accessibility Requirements:
- Wheelchair accessible entrances and pathways: Entrances must be level or ramped with a maximum slope of 1:20, ensuring smooth and effortless access for wheelchair users. Pathways must be wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs comfortably and have firm, stable surfaces.
- Accessible parking spaces: A minimum of 2% of the total parking capacity must be designated as accessible parking, located close to building entrances with ample space for maneuvering.
- Elevator requirements: Buildings over two stories are required to have elevators that meet specific accessibility standards, including appropriate dimensions, controls, and signage.
- Accessible restroom facilities: Restrooms must include features such as grab bars, accessible sinks, and adequate turning space within the stalls. Specific dimensional requirements ensure comfortable and safe usage.
- Visual and auditory accessibility features: Public buildings must incorporate features such as tactile paving, braille signage, audio announcements, and assistive listening systems to cater to people with visual and auditory impairments.
Benefits of Adhering to Accessibility Standards (Pros):
- Legal compliance: Meeting these requirements ensures compliance with UAE federal accessibility laws, avoiding potential penalties and legal complications.
- Expanded market reach: Designing accessible buildings opens the door to a wider customer base, including people with disabilities and their families.
- Enhanced corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile: Demonstrating a commitment to accessibility strengthens a company's CSR profile and contributes to a positive brand image.
- Future-proofing against demographic changes: As the population ages, the demand for accessible buildings will only increase. Incorporating accessibility features now future-proofs buildings for long-term viability.
Challenges of Implementing Accessibility Features (Cons):
- Additional design complexity and space requirements: Integrating accessibility features can add complexity to the design process and may require additional space allocation.
- Increased construction costs: Specialized accessibility equipment and features can increase construction costs. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
- Ongoing maintenance of specialized equipment: Accessibility equipment, such as elevators and automatic door openers, requires regular maintenance to ensure proper functionality.
- Potential aesthetic design limitations: Some developers may perceive accessibility features as limiting design aesthetics. However, with careful planning and creative solutions, accessibility can be seamlessly integrated into aesthetically pleasing designs.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Dubai Metro stations: The Dubai Metro system exemplifies comprehensive accessibility design, with ramps, elevators, tactile paving, and audio announcements facilitating seamless travel for everyone.
- Dubai International Airport: Award-winning accessibility features at Dubai International Airport, including dedicated assistance services and accessible facilities, make it a global leader in accessible air travel.
- City Walk development: City Walk, a popular lifestyle destination, incorporates universal design principles, creating a welcoming and inclusive environment for all visitors.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Integrate accessibility from the start: Incorporate accessibility features into the initial design phase rather than retrofitting later, which can be significantly more costly and complex.
- Consult with disability advocacy groups: Engaging with disability advocacy groups during the planning process provides valuable insights and ensures that the design truly meets the needs of diverse users.
- Staff training: Train staff on accessibility features and procedures for assisting people with disabilities, fostering a welcoming and supportive environment.
- Regular maintenance: Implement a schedule for regular maintenance and testing of all accessibility equipment to ensure continued functionality and safety.
By embracing these accessibility standards, builders and developers in the UAE contribute not only to legal compliance but also to a more inclusive and equitable society. Dubai Municipality and the UAE Ministry of Community Development have championed these initiatives, providing resources and guidance for implementing accessibility effectively. Investing in accessibility is an investment in the future, creating a city that welcomes and empowers everyone.
5. High-Rise Building Regulations
Dubai's skyline is a testament to its ambition and engineering prowess, boasting some of the world's tallest and most iconic structures. This architectural marvel is made possible by, and dependent upon, stringent high-rise building regulations that address the unique challenges inherent in constructing and maintaining these vertical behemoths. These regulations deserve a prominent place on this list of Dubai building codes because they directly impact the safety, functionality, and sustainability of the city's most defining feature: its skyline. Specifically, these codes address critical aspects such as wind engineering, vertical transportation, emergency evacuation, and maintenance access, ensuring these structures are not just impressive, but also safe and operational. This section will delve into the intricacies of these high-rise regulations, highlighting their importance for anyone involved in the construction and management of tall buildings in Dubai.
Dubai's high-rise building code goes beyond standard building regulations, incorporating advanced engineering principles and international best practices. Buildings exceeding 150 meters are subject to rigorous wind tunnel testing to ensure structural stability against the strong winds common in the region. The regulations also mandate specialized elevator and escalator safety standards, along with enhanced structural monitoring systems to detect any potential issues early on. For super-tall buildings, helicopter landing facilities are often required for emergency access and evacuation. Furthermore, progressive collapse prevention measures are integrated into the design to minimize the risk of cascading structural failure in the event of an unforeseen incident.
The benefits of these stringent regulations are clear: world-class safety standards for tall building construction, enhanced emergency response capabilities, and structural integrity assurance at extreme heights. Dubai’s adherence to international best practices ensures that its high-rise buildings are among the safest in the world. Examples of successful implementations abound, including the Burj Khalifa’s pioneering high-rise safety systems, the Burj Al Arab’s unique structural and safety design, and the Dubai Frame’s innovative high-rise engineering solutions. These structures stand as testaments to the effectiveness of Dubai’s high-rise regulations.
However, adhering to these regulations comes with challenges. The highly specialized nature of high-rise construction leads to extremely high compliance costs for testing and certification. Design and approval timelines can be extensive due to the complexity of the projects and the thorough reviews required. The limited pool of qualified specialists can also pose a challenge, requiring developers to engage international experts early in the planning process. Furthermore, the ongoing maintenance requirements for these complex structures are substantial.
For those involved in high-rise projects in Dubai, several tips are crucial. Engaging international high-rise specialists early in project planning is essential for navigating the complexities of the regulations. Budgeting significant resources for wind tunnel testing and analysis is unavoidable. Planning for specialized construction equipment and techniques is also necessary, given the unique challenges of high-rise construction. Finally, establishing comprehensive building management protocols is paramount for the long-term safety and functionality of these structures.
The following infographic illustrates the streamlined, three-step process for compliance with key aspects of Dubai's High-Rise Building Regulations. This simplified representation highlights the critical stages involved in ensuring the structural integrity and safety of tall buildings.
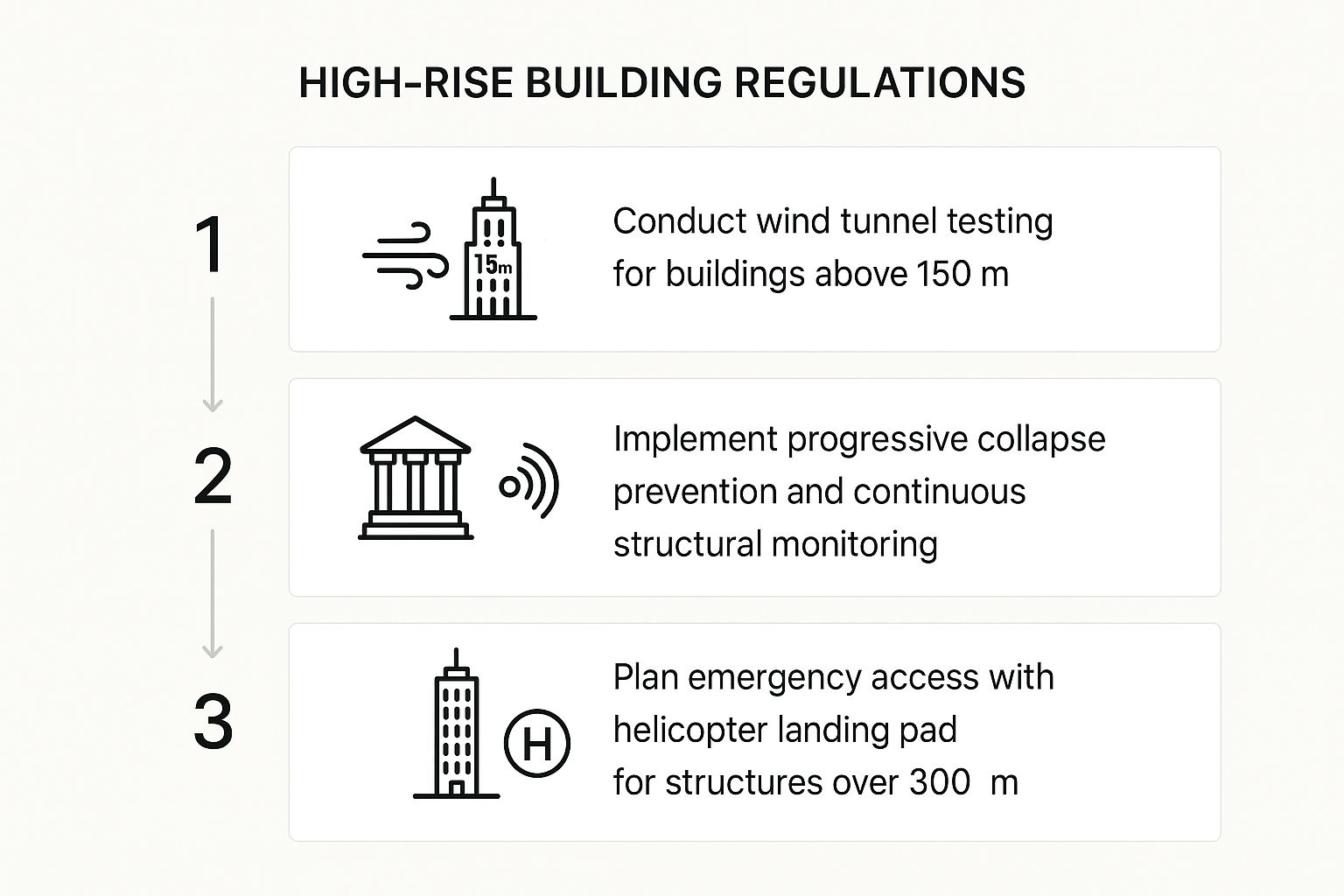
The infographic clearly outlines the sequential process, starting with wind tunnel testing for buildings over 150 meters, followed by the implementation of progressive collapse prevention and structural monitoring, and culminating in the planning of emergency access, including helicopter landing pads for structures exceeding 300 meters. The interconnectedness of these steps underscores the importance of a holistic approach to high-rise building safety in Dubai.
Dubai's high-rise building regulations are a critical component of the city's construction landscape. While the regulations present challenges in terms of cost and complexity, the resulting benefits in safety, functionality, and international best practice compliance are undeniable. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, developers and building managers contribute to a safer and more sustainable future for Dubai's iconic skyline. Organizations like Emaar Properties, Dubai Municipality, and the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat have played a crucial role in popularizing and refining these essential guidelines, helping to shape Dubai's unique urban environment.
6. Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Code
Dubai's demanding climate and rapid infrastructural development necessitate stringent building codes, and the Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) code plays a crucial role in ensuring functionality, safety, and sustainability. This code establishes comprehensive standards for the design, installation, and maintenance of building systems, encompassing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), electrical installations, plumbing, and drainage. Adhering to the Dubai building codes, specifically the MEP regulations, is not just a legal obligation but also a vital step towards creating efficient, resilient, and comfortable built environments within the challenging Gulf climate. This section explores the intricacies of Dubai's MEP code and its implications for various stakeholders in the construction and facilities management sectors.
The MEP code serves as a blueprint for achieving several critical objectives in building design and operation. It mandates the use of energy-efficient technologies, reducing the overall environmental footprint of buildings and minimizing operational costs. Furthermore, the code prioritizes occupant health and safety by establishing rigorous standards for electrical installations, fire safety systems, and sanitation. In a region characterized by extreme summer temperatures, the MEP code is paramount in ensuring indoor environments remain comfortable and conducive to productivity. Finally, the regulations promote the adoption of sustainable practices such as greywater recycling, thereby conserving valuable resources and contributing to Dubai's ambitious sustainability goals.
Features of the MEP code related to Dubai building codes include stipulations for energy-efficient HVAC systems with minimum Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) ratings. This promotes the use of advanced cooling technologies that minimize energy consumption while delivering optimal cooling performance. Electrical safety is another focal point, with the code prescribing standards for wiring, surge protection, and emergency power systems. Water conservation is also addressed through requirements for low-flow plumbing fixtures and efficient irrigation systems. In larger developments, the code often mandates greywater recycling systems, further reducing water consumption. Increasingly, the MEP code also incorporates provisions for smart building integration, allowing for centralized control and optimization of building systems.
The implementation of Dubai's MEP code offers a range of benefits. Reduced utility costs are a primary advantage, achieved through the use of energy and water-efficient systems. Enhanced occupant comfort and health are assured by maintaining optimal indoor air quality and thermal comfort. The emphasis on sustainability results in a lower environmental impact, aligning with Dubai's green building initiatives. Moreover, adherence to the code enhances building reliability and longevity, minimizing the need for costly repairs and replacements.
However, meeting these stringent standards can present some challenges. The initial installation costs for high-efficiency systems can be higher compared to conventional systems. The complexity of system integration and controls may require specialized expertise during design and implementation. Ongoing maintenance also requires skilled technicians familiar with the advanced technologies employed. Finally, periodic system upgrades may be necessary to maintain optimal efficiency and comply with evolving regulations.
Examples of successful MEP code implementation can be seen in landmark projects across Dubai. The Dubai Opera, for instance, boasts a sophisticated MEP system designed for optimal acoustic performance and precise climate control. Ibn Battuta Mall, a sprawling retail complex, exemplifies large-scale efficient MEP implementation, managing the energy demands of a high-traffic environment. Dubai Healthcare City, with its specialized medical facilities, showcases MEP systems designed for critical environments with stringent hygiene and safety requirements.
For those involved in building projects in Dubai, adhering to the MEP code requires careful planning and execution. Designing MEP systems to withstand Dubai's extreme summer temperatures is crucial. Implementing preventive maintenance programs from the outset ensures long-term efficiency and reliability. Leveraging building automation systems can optimize energy consumption and enhance operational control. Selecting contractors with UAE-specific MEP experience is also essential for successful project delivery. Learn more about Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Code
In conclusion, the MEP code holds a significant place within the Dubai building codes framework. Its comprehensive regulations address crucial aspects of building performance, impacting everything from energy efficiency and occupant comfort to environmental sustainability and long-term building value. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, stakeholders in Dubai's construction and facilities management sectors can contribute to the creation of a built environment that is both high-performing and environmentally responsible.
7. Swimming Pool and Water Feature Safety Code
Dubai's reputation for luxury living often features stunning swimming pools and elaborate water features. However, these aquatic amenities come with significant responsibility. The Swimming Pool and Water Feature Safety Code, a crucial component of Dubai's building codes, addresses the specific safety and hygiene concerns associated with these attractions, aiming to prevent accidents and protect public health. This code deserves its place in Dubai's building codes due to the prevalence of pools and water features in the region, the inherent risks they pose, and the importance of maintaining high safety standards in a city known for its world-class infrastructure.
The code encompasses a wide range of specifications, including design, construction, operation, and maintenance of swimming pools, spas, water parks, and other water features. It mandates adherence to strict guidelines regarding safety barriers, water quality, drainage systems, and emergency equipment. This detailed approach is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it minimizes the risk of drowning, especially among children, who are particularly vulnerable in aquatic environments. Secondly, it ensures that water quality remains consistently high, mitigating health risks associated with contaminated water. Finally, it promotes overall safety and well-being within these recreational spaces.
Key Features of the Swimming Pool and Water Feature Safety Code:
- Mandatory Safety Barriers: Perhaps the most visible element of the code is the requirement for robust safety barriers surrounding all swimming pools and water features. These barriers must be of a specified height, have self-closing and self-latching gates, and be designed to prevent unauthorized access, especially by young children.
- Pool Depth Markings and Non-Slip Surfaces: Clear depth markings are mandated at various points around the pool to inform users of the water depth. Non-slip surfaces are required around the pool perimeter and within the pool itself to prevent slips and falls.
- Water Circulation and Filtration System Standards: The code sets strict standards for water circulation and filtration systems to maintain optimal water hygiene and prevent the spread of waterborne diseases. This includes requirements for regular cleaning, disinfection, and water quality testing.
- Emergency Equipment: The code mandates the provision of essential emergency equipment, such as life rings, reaching poles, and readily accessible first aid stations. This equipment plays a vital role in responding quickly to accidents and potentially saving lives.
- Lighting Requirements: Adequate lighting is required for all swimming pools and water features, especially for those open during nighttime hours. This ensures visibility and enhances safety for users.
Pros and Cons of Implementing the Code:
Pros:
- Significant reduction in drowning incidents: The stringent safety measures contribute significantly to reducing the risk of drowning.
- Improved water quality and hygiene: The code leads to better water quality, promoting public health and preventing waterborne illnesses.
- Enhanced property insurance coverage: Compliance with the code can positively impact property insurance premiums.
- Compliance with international aquatic safety standards: Adhering to these codes aligns with international best practices in aquatic safety.
Cons:
- Additional construction costs for safety features: Implementing these safety measures can add to the initial construction costs.
- Ongoing maintenance and water treatment expenses: Maintaining the required safety features and water quality involves ongoing operational costs.
- Design limitations due to safety requirements: The safety requirements might impose certain design limitations.
- Regular testing and compliance monitoring needed: Compliance with the code requires regular testing and monitoring, adding to the administrative burden.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Atlantis The Palm: This iconic resort showcases comprehensive aquatic safety systems, demonstrating a commitment to guest safety.
- Dubai Marina residential towers: Many residential towers in Dubai Marina have implemented robust pool safety measures, adhering to the code's requirements.
- Wild Wadi Waterpark: This popular waterpark employs advanced safety and filtration systems, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience for visitors.
Actionable Tips for Compliance:
- Install pool safety features during initial construction: Integrating safety features during the construction phase is more cost-effective than retrofitting later.
- Implement regular water testing and treatment protocols: Establish a routine schedule for water testing and treatment to ensure consistent water quality.
- Provide clear safety signage in multiple languages: Display prominent safety signage in multiple languages to cater to Dubai's diverse population.
- Train facility staff in water rescue and first aid: Equip staff with the necessary skills to respond effectively in emergencies.
The Dubai Municipality and the Dubai Health Authority are key entities responsible for promulgating and enforcing this code. While adherence to the Swimming Pool and Water Feature Safety Code may present some initial challenges and expenses, its benefits in terms of enhanced safety and public health are undeniable. For all stakeholders involved in the construction, management, and use of aquatic facilities in Dubai, understanding and complying with this code is paramount. It represents a significant step towards creating safer and healthier aquatic environments for residents and visitors alike.
8. Seismic Design and Earthquake Resistance Standards
Dubai, with its ambitious skyline and rapid development, recognizes the importance of building not just for aesthetic appeal, but also for resilience against natural forces. While the UAE isn't located within a highly active seismic zone, the potential for moderate earthquakes originating from nearby regions necessitates adherence to stringent seismic design and earthquake resistance standards within Dubai's building codes. This is particularly crucial for preserving the structural integrity of high-rise structures, safeguarding occupants, and ensuring the continuity of essential services in critical facilities. This section delves into the importance of these standards within Dubai's building codes and provides practical insights for stakeholders involved in the construction and maintenance of buildings within the emirate.
Dubai's seismic design code outlines a comprehensive framework for constructing earthquake-resistant buildings. This involves using specific construction methods and materials designed to withstand ground motion during seismic events. The code adheres to and incorporates internationally recognized best practices, ensuring that structures in Dubai meet global safety standards. This approach is essential not only for mitigating damage during an earthquake but also for minimizing long-term repair costs and ensuring the longevity of the building.
The seismic design code in Dubai functions by classifying different areas within the emirate based on their seismic risk. This zoning system dictates specific design requirements tailored to the anticipated ground motion in each zone. Buildings in higher-risk zones are subject to more stringent regulations. The code specifies requirements for:
- Flexible Building Connections and Expansion Joints: These features allow the building components to move slightly during an earthquake, reducing stress on the overall structure and minimizing the risk of catastrophic failure.
- Reinforced Concrete and Steel Specifications for Seismic Loads: The code dictates the quality, type, and placement of reinforcement within concrete and steel structures to ensure they can withstand the forces generated during a seismic event.
- Base Isolation Systems for Critical Infrastructure: For particularly sensitive structures like hospitals and power plants, base isolation systems are often required. These systems effectively decouple the building from the ground, absorbing much of the seismic energy and drastically reducing the impact on the superstructure.
Seismic assessments are not limited to new constructions. Existing buildings are also subject to regular seismic evaluations to ensure they continue to meet the evolving safety standards outlined in the Dubai building codes. This proactive approach allows for timely identification of potential vulnerabilities and implementation of necessary retrofits, strengthening the city’s overall resilience against seismic activity.
Examples of successful implementations of these seismic design principles in Dubai include:
- Dubai International Airport: The airport's terminals incorporate robust seismic-resistant design features, ensuring the continuous operation of this critical transportation hub even in the event of an earthquake.
- Dubai Healthcare City: Given the essential nature of healthcare facilities, buildings within Dubai Healthcare City are designed with stringent seismic protection measures to guarantee uninterrupted service during emergencies.
- Business Bay Towers: The numerous high-rise towers in Business Bay exemplify the integration of seismic design principles into modern commercial construction.
Actionable tips for adherence to Dubai’s seismic building codes:
- Conduct Thorough Seismic Hazard Analysis: A site-specific seismic hazard analysis is crucial for understanding the specific risks and designing appropriate mitigation measures.
- Engage Qualified Structural Engineers: Working with experienced structural engineers specializing in seismic design is essential for ensuring compliance with the codes and achieving optimal structural performance.
- Consider Base Isolation: For critical facilities or buildings with high occupancy, investing in base isolation systems can significantly enhance safety and reduce potential damage.
- Implement Regular Structural Health Monitoring: Continuous monitoring systems can provide valuable data on the structural integrity of a building, allowing for early detection of potential issues and timely intervention.
Why are seismic considerations important in Dubai's building codes?
While the UAE may not be prone to frequent, high-magnitude earthquakes, the potential for tremors originating from nearby seismically active regions necessitates proactive measures. The consequences of neglecting seismic design can be devastating, potentially leading to structural damage, economic losses, and, most importantly, loss of life. The inclusion of earthquake resistance in Dubai's building codes demonstrates the commitment to safeguarding public safety, protecting investments, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the built environment. The rigorous implementation of these standards, promoted by entities like Dubai Municipality and guided by international best practices from organizations like the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), establishes a framework for creating a resilient and safe urban landscape in Dubai. By adhering to these codes, stakeholders in the construction industry contribute to a more secure future for the city.
Dubai Building Codes: Key Regulation Comparison
| Code / Regulation | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dubai Building Code (DBC) - Structural Safety Requirements | High due to detailed load, seismic, and material specs | Specialized engineering expertise, comprehensive soil testing | Enhanced public safety, reduced maintenance costs, higher property value | Multi-story buildings, high-rise towers in seismic/windy areas | Rigorous safety standards, international recognition |
| Fire Safety and Life Protection Code | Moderate to high, integrating fire systems and evacuation plans | Investment in fire prevention/detection systems, training | Significantly reduced casualties/damage, improved emergency response | Commercial, residential, public buildings over 18m height | Improved occupant safety, insurance benefits |
| Energy Efficiency and Green Building Standards | High due to technical design and renewable integration | Certified consultants, green materials, energy monitoring | Energy savings, reduced environmental impact, sustainable buildings | New developments aiming for sustainability and cost reduction | Lower operational costs, marketability increase |
| Accessibility and Universal Design Requirements | Moderate, requires detailed design integration | Specialized design, accessibility equipment, staff training | Legal compliance, inclusivity, broader market reach | Public, commercial, and residential buildings serving diverse users | Compliance with federal laws, social responsibility |
| High-Rise Building Regulations | Very high, includes advanced wind, evacuation, and monitoring | High costs for testing, specialized equipment, experts | World-class safety, structural integrity at extreme heights | Super-tall buildings, skyscrapers | Best practice safety, emergency preparedness |
| Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Code | Moderate, complex system integration and controls | Skilled contractors, energy-efficient and smart systems | Reduced utility costs, occupant comfort, environmental benefits | Large buildings requiring efficient HVAC, electrical, plumbing | Enhanced building reliability, sustainability |
| Swimming Pool and Water Feature Safety Code | Moderate, safety and hygiene features integration | Safety barriers, filtration, emergency equipment | Reduced accidents, improved water quality, insurance benefits | Residential and commercial pools, aquatic facilities | Drowning prevention, international safety compliance |
| Seismic Design and Earthquake Resistance Standards | High, specialized seismic calculations and materials | Seismic engineers, advanced materials, ongoing assessments | Enhanced building stability, reduced damage, occupant safety | High-risk seismic zones, critical infrastructure, high-rise | Alignment with international seismic standards |
Partnering for Success: Yasu Trading Co. LLC and Dubai's Building Codes
Navigating the complexities of Dubai's building codes is crucial for any construction project in the emirate. From ensuring structural integrity and fire safety to meeting energy efficiency targets and accessibility standards, adhering to these codes is paramount for project success and the safety and well-being of occupants. This article has highlighted key aspects of the Dubai building codes, encompassing structural requirements, fire safety, green building practices, accessibility, high-rise regulations, MEP standards, swimming pool safety, and seismic design considerations. Mastering these concepts is not merely a regulatory checkbox, but a fundamental step towards building sustainable, resilient, and safe structures that contribute to Dubai's world-class urban landscape. Understanding and implementing these codes ensures compliance, minimizes risks, and ultimately fosters a more secure and prosperous built environment for all.
For construction companies, general contractors, real estate developers, and all stakeholders involved in the building process in the UAE, compliance with Dubai building codes is non-negotiable. This requires access to high-quality materials and expert guidance. Successfully navigating these codes is essential not only for legal compliance but also for creating durable, safe, and efficient buildings. This knowledge empowers professionals to build with confidence, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable urban environment in Dubai.
Yasu Trading Co. LLC, located in Dubai’s Nakheel Center, understands these challenges and offers a comprehensive solution. We provide a wide selection of premium building hardware and construction essentials, all meticulously chosen to meet the strict standards of Dubai building codes. From structural steel and plumbing fixtures to fire-rated doors and energy-efficient lighting, we equip you with the necessary tools and expertise to build compliant and successful projects. Visit Yasu Trading Co. LLC today to discuss your specific project needs and let us help you navigate Dubai's building codes with confidence.