Hybrid Hoses & Couplings: Selecting the Right Hose for Industrial Projects
Choosing the right hybrid hose and coupling for an industrial project is more than just a matter of matching sizes. It's a decision that has a direct line to your operation's safety, efficiency, and uptime. Making a confident choice comes down to a systematic look at the core criteria: size, temperature, application, media, and pressure. Get these right, and you've built an assembly that can handle whatever the job throws at it.
Your Foundation for Industrial Hose Selection
Picking the correct industrial hose is the bedrock of a successful project. Get it wrong, and you’re setting yourself up for failure. Hybrid hoses, which often blend materials like PVC, rubber, and polyurethane, are popular for good reason. They offer a great mix of flexibility, durability, and resistance to the rough-and-tumble conditions you see in construction, manufacturing, or oil and gas.
But you only get those benefits if your selection process is on point.

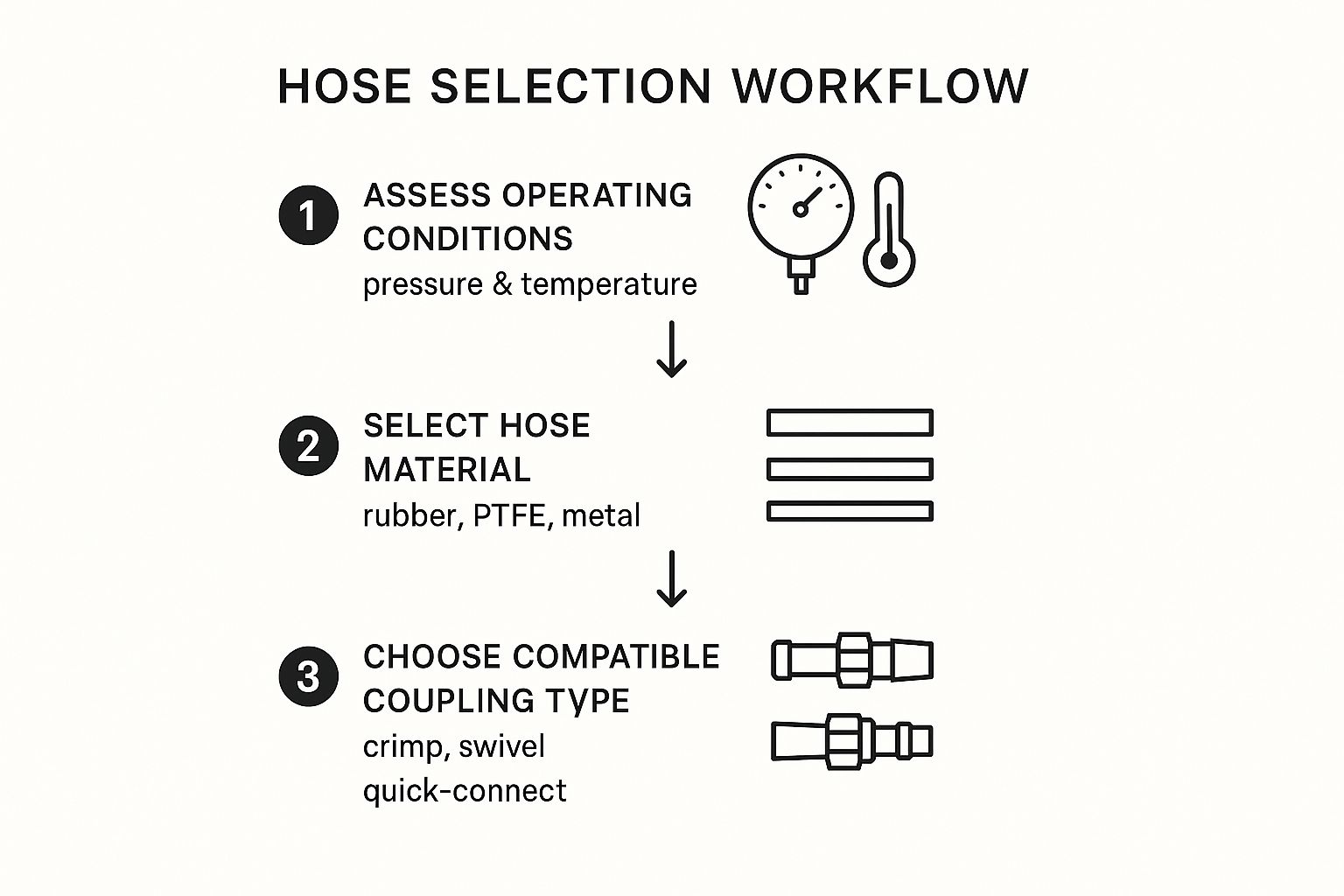
This is where an industry-proven framework called the STAMPED method comes into play. Think of it as your pre-flight checklist. It forces you to stop and consider every critical variable before you spend a dime. If you skip even one of these steps, you're risking premature wear, surprise leaks, or a catastrophic failure—all of which lead to expensive downtime and serious safety hazards.
The STAMPED Method Explained
The STAMPED method is a simple but incredibly effective tool. It walks engineers and project managers through a set of questions that paint a complete picture of what the hose assembly will face on the job.
Here’s the breakdown:
- Size: What are the inner and outer diameters? What length do you need?
- Temperature: What’s the temperature of the material running through it? What about the ambient temperature around it?
- Application: How is this hose actually going to be used? Is it a static line, or is it going to be flexed, dragged, and abused all day?
- Media: What are you pumping? Is it corrosive, abrasive, or something volatile?
- Pressure: What’s the maximum working pressure? And just as important, are there any surges or spikes to account for?
- Ends: What kind of couplings or fittings do you need for a secure, leak-proof connection?
- Delivery: Are there any special needs, like specific packaging, testing, or certifications?
The infographic above really hammers home the starting point. Before you can even think about materials or couplings, you absolutely have to understand your operational environment—especially the pressure and temperature demands.
Applying the Framework in the Field
Knowing how to measure pipe diameter accurately is a fundamental skill, and it’s critical for getting the "Size" part of STAMPED right. One wrong measurement can make the entire exercise useless. When you methodically work through each letter, you build a detailed spec sheet that leaves no room for guesswork.
To really see this in action, it helps to use a framework. The STAMPED method gives you a repeatable process to make sure you've covered all your bases for any project.
The STAMPED Method for Hose Selection
Use this framework to systematically address every critical factor when selecting an industrial hose, ensuring no detail is overlooked.
| Factor | Key Questions to Ask | Example Industrial Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Size | What is the required inner diameter for the flow rate? How long does the hose need to be to avoid tension? | A construction site needs a 2-inch ID hose, 50 meters long, to transfer water from a dewatering pump without stretching. |
| Temperature | Will the hose be exposed to extreme ambient heat or freezing conditions? What is the temperature of the fluid? | A manufacturing plant needs a hose to carry cooling water at 80°C through a factory floor where ambient temperatures reach 45°C. |
| Application | Will the hose be dragged across abrasive surfaces like concrete or gravel? | A mining operation requires a durable slurry hose that can withstand being dragged over rough terrain daily. |
| Media | What chemicals or fluids will pass through the hose? Are they compatible with the inner tube material? | An agricultural project uses a hose to spray fertilizers containing ammonia, requiring a chemically resistant liner. |
| Pressure | What is the system's maximum working pressure, and are there pressure spikes during pump start-up? | A hydraulic system operates at 3,000 PSI, with potential surges up to 3,500 PSI, demanding a high-pressure rated hose. |
| Ends | What type of fittings are needed to connect to the pump and nozzle? Do they need to be corrosion-resistant? | A chemical transfer application requires stainless steel camlock fittings to ensure material compatibility and quick connection. |
| Delivery | Does the hose need to be certified for a specific standard, like food-grade or petroleum transfer? | A food processing facility requires a hose with FDA-compliant certification, delivered with full traceability documentation. |
By walking through these questions every single time, you create a solid, defensible specification for your hose assembly.
Consistently applying the STAMPED methodology is what separates the pros from the amateurs. It moves you from making a guess to making an evidence-based decision, which is your best defense against assembly failure.
Getting to Know Hybrid Hose Materials and Specs
The term "hybrid" isn't just marketing jargon when it comes to industrial hoses. It points to a smart combination of materials, each chosen to do a specific job better than any single material could alone. Getting a handle on this blend is the first step in picking the right hose, as it directly affects everything from durability and flexibility to how well it stands up to harsh chemicals.
Think of it like a team: the inner tube handles the fluid, the reinforcement provides strength, and the outer cover takes a beating from the environment.

This material synergy is what gives a hybrid hose its real-world advantage. For example, you might find a hose with a nitrile inner tube for excellent chemical resistance, wrapped in a tough-as-nails polyurethane cover. That specific combo is perfect for moving petroleum fluids on a rough construction site, a job that would tear a standard PVC or rubber hose to shreds in no time.
Decoding Common Hybrid Hose Materials
When you're looking at hybrid hoses and couplings, you'll keep seeing the same few materials pop up. Each one brings something different to the table.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): This is a popular, cost-effective choice. It's lightweight and holds up well against water and a lot of common chemicals, making it a great all-rounder for general-purpose work.
- Polyurethane (PU): If your hose is going to be dragged across concrete, gravel, or other rough surfaces, you want polyurethane in the mix. It's the king of abrasion resistance, which is why it's a favorite on construction and mining sites.
- Nitrile Rubber (NBR): Got oil, fuel, or grease? Nitrile is your answer for the inner tube. It’s designed to resist those petroleum-based products without swelling up or breaking down.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): For jobs involving extreme heat, cold, or constant sun exposure, EPDM is the star player. It's fantastic for handling hot water and steam, and it won't crack under UV and ozone exposure.
The real magic happens when these materials are combined. You could have a hose with an EPDM tube for high-temp fluids, beefed up with a high-tensile synthetic cord, and then wrapped in a rugged polyurethane cover. That’s a level of performance you just can't get from a single-material hose.
Reading Technical Data Sheets Like a Pro
That technical data sheet (TDS) is your roadmap, but it can look like a foreign language at first. The trick is to ignore the noise and zero in on the specs that directly impact safety and performance.
The numbers on a data sheet aren't suggestions; they're hard limits. Pushing a hose past its working pressure or temperature range is a surefire way to cause a failure, and that's a massive safety risk.
Here’s what you need to focus on:
- Working Pressure: This tells you the maximum pressure the hose can safely handle day in and day out. Your system's operating pressure should always be lower than this number.
- Burst Pressure: This is the point of no return—the pressure at which the hose is designed to fail. It's usually three to four times higher than the working pressure, giving you a critical safety buffer.
- Bend Radius: This number tells you how tightly you can bend the hose before it kinks or gets damaged. Ignoring it will restrict flow and create a weak spot.
- Material Certifications: Always check for certifications relevant to your job. This could be FDA compliance for a food-grade hose or specific ratings for handling volatile chemicals.
Environmental Factors and Material Selection
Don't just think about what's inside the hose; the outside world matters just as much. A hose baking in the UAE summer sun faces a very different set of challenges than one used in a climate-controlled factory.
For instance, PVC-based hoses are gaining a lot of traction on industrial projects across the MEA region because they're light, chemical-resistant, and don't break the bank. The Middle East and Africa PVC hose market hit a value of around USD 19.7 million, and it's expected to keep growing, showing just how well it’s been adopted for industrial irrigation and chemical transfer. You can find more details about the PVC hose market on Cognitive Market Research.
Abrasive dust, UV radiation, and corrosive spills all chip away at a hose's lifespan. That's why a tough outer cover is non-negotiable. On a quarry site, a simple rubber cover would get chewed up fast. A hybrid hose with a polyurethane or UHMWPE (ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene) cover has the grit to survive being dragged over sharp rocks, which means it lasts longer and gives you a better return on your investment.
Matching Couplings to Hoses and Applications
A top-tier hybrid hose is only as good as its coupling. It’s the critical link in the chain—if that connection point fails, the whole assembly is useless. Getting a secure, leak-proof seal is non-negotiable for both safety and efficiency, which means we need to look past generic options and get specific about what works in real-world industrial settings.

The success of your entire system really does hinge on this final piece of the puzzle. A mismatch in materials, threads, or pressure ratings is a recipe for leaks, expensive downtime, or even a dangerous blowout. It’s a detail that absolutely demands your full attention.
Aligning Coupling Material With Media and Environment
The first rule of thumb when selecting hybrid hoses & couplings is always material compatibility. The coupling has to stand up to whatever you're running through it, plus whatever the external environment throws at it. Get this wrong, and you're looking at corrosion, contamination, and a coupling that fails way sooner than it should.
Take transferring corrosive chemicals, a common job on many sites. Slapping on a standard brass or aluminum coupling here would be a huge mistake; the material would degrade in no time. For anything aggressive, stainless steel is the go-to choice because of its fantastic corrosion resistance. If you want to dig deeper into why, our guide on the advantages of stainless steel pipe fittings is a great resource.
Here’s a quick rundown of the most common materials I see in the field:
- Stainless Steel: Your best bet for corrosive chemicals, high-purity systems, and food-grade applications. It’s tough and handles high temperatures like a champ.
- Brass: A solid, budget-friendly option for non-corrosive stuff like air, water, and oil. It’s plenty durable for most general-purpose jobs.
- Aluminum: Its main selling point is being lightweight. This makes it a great fit for fuel transfer or any application where you’re constantly moving hoses around. Just know that it’s softer and won’t take the same abuse as steel or brass.
- Polypropylene: This plastic option offers excellent resistance to certain acids and caustics. It’s light and cost-effective but comes with lower pressure and temperature limits.
Common Industrial Coupling Types and Their Ideal Applications
Choosing the right type of industrial hose coupling is just as crucial as selecting the right hose. A direct comparison can help you pinpoint the most effective option for your project's unique demands. The table below breaks down the common styles I see on job sites every day.
| Coupling Type | Primary Material | Best For | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camlock | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Brass, Polypropylene | Rapid transfer of liquids and powders where you need to connect and disconnect often. | Not safe for compressed air or steam. The risk of accidental disconnection under pressure is too high. |
| Quick-Disconnect | Steel, Brass, Stainless Steel | Pneumatic tools, hydraulic lines, and any fluid line requiring fast, tool-free changes on the fly. | Pressure ratings can vary wildly by design. Always double-check the rating for your specific application. |
| Ground Joint | Plated Steel, Stainless Steel | High-pressure, high-temperature jobs, especially steam or compressed air service. | Creates a very secure connection with a tight, mechanical seal between metal surfaces. |
| Threaded (NPT/BSPT) | Brass, Steel, Stainless Steel | Permanent or semi-permanent connections that you don't plan on changing frequently. | Mismatched threads (like NPT vs. BSPT) are a classic rookie mistake and a very common cause of leaks. |
Ultimately, the goal is to create a secure and efficient connection. Understanding these differences ensures you select a coupling that not only fits but also enhances the safety and performance of your entire system.
Choosing the Right Attachment Method
Once you've zeroed in on the material and style, the next question is how the coupling will actually attach to the hose. The three main methods you'll encounter each have their own place.
Permanently Crimped Fittings
For high-pressure or critical applications, this is the gold standard. A hydraulic crimper is used to squeeze a metal collar (the ferrule) over the hose, creating a permanent, 360-degree seal. This method gives you the most secure and reliable connection possible, making it the only real choice for things like hydraulic systems or when you're moving hazardous materials.
Reusable or Field-Attachable Fittings
These are your problem-solvers in the field. They can be attached with basic hand tools, which is perfect for making on-the-spot repairs and keeping downtime to a minimum. They're incredibly convenient, but keep in mind they generally can't handle the same high pressures as a crimped fitting. Think air lines or general water transfer—situations where a quick fix is more valuable than a high-pressure rating.
Band Clamps
You’ll see these on lower-pressure jobs. A band is tightened around the outside of the hose to clamp down on a barbed fitting inside. They work just fine for simple tasks, but you would never use them for high-pressure systems or in any scenario where a failure would be catastrophic.
Here’s a critical safety tip I can’t stress enough: The pressure rating of your entire hose assembly is only as strong as its weakest link. A 4,000 PSI hose paired with a 1,000 PSI coupling is a 1,000 PSI assembly, period. Never assume the hose's rating is the system's rating.
Navigating Pressure and Temperature Demands
In any industrial setting, pressure and temperature are the two forces you can't afford to get wrong. A miscalculation here isn’t just a minor hiccup; it can quickly spiral into a catastrophic failure, bringing operations to a grinding halt and putting people at serious risk. Getting these ratings right isn't just a technical box-ticking exercise—it's one of the most fundamental safety protocols you can follow.
When you're looking at specs, it's easy to get lost in the numbers. But the pressure rating on a hose isn't a single, simple figure. It’s actually a set of three distinct benchmarks that spell out its operational limits and, crucially, its safety buffer.
Understanding Pressure Ratings
When you scan the technical data for hybrid hoses & couplings, you'll find a few different pressure ratings. Knowing what each one means is non-negotiable.
- Working Pressure: Think of this as your everyday limit. It's the maximum continuous pressure the hose assembly is built to handle safely, day in and day out. Your system’s normal operating pressure should never exceed this number.
- Proof Pressure: This is a factory-test value. The manufacturer subjects the hose to a short burst of pressure, usually double the working pressure, to make sure there are no hidden weaknesses or leaks from the get-go.
- Burst Pressure: This is the absolute breaking point—the pressure at which the hose is engineered to fail. It’s typically three to four times the working pressure and acts as your ultimate safety net.
In the field, a 4:1 safety factor is the gold standard. This means the hose’s burst pressure should be at least four times your system’s maximum working pressure. This buffer is what saves you from unexpected pressure spikes and the slow, invisible wear and tear of material fatigue.
The Critical Role of Temperature De-Rating
Here’s something that trips up even experienced teams: the impact of heat on a hose's strength. As the temperature of the fluid inside—or the air outside—climbs, the hose material softens and loses some of its muscle. This directly lowers the amount of pressure it can safely handle.
This is where temperature de-rating becomes essential. Manufacturers provide charts that show you exactly how much you need to reduce the maximum working pressure as temperatures rise above the standard baseline (which is usually around 21°C).
For example, a hose rated for 2,000 PSI at room temperature might only be safe up to 1,200 PSI when it’s carrying fluid at 90°C. Simply ignoring this fact is a recipe for disaster, especially given the high ambient heat we often face on projects in this region. To get it right, you need to properly size your system by consulting a guide on how to read a pipe size chart and then apply these critical de-rating factors.
Real-World Scenarios and Risks
Let's put this into a real-world context. Imagine a construction crew using a high-pressure water jetting system that runs at 3,000 PSI. They’ve picked a hose with a 3,500 PSI working pressure rating, thinking they've built in a decent safety margin. The problem? That hose is often left baking in the sun on a hot summer afternoon, with its surface temperature easily hitting 70°C.
Without factoring in temperature de-rating, they don't realize that the hose's actual safe working pressure has plummeted to around 2,500 PSI. They are now running the system 500 PSI over its true limit. The risk of a sudden, violent burst has just skyrocketed, endangering anyone nearby and threatening to damage expensive equipment.
The demand for high-performance industrial hoses is surging across the Middle East and Africa, driven by massive projects in oil & gas and construction. The market recently hit about USD 1.29 billion and is forecast to reach nearly USD 1.87 billion by 2030. This growth underscores the urgent need for materials that can stand up to extreme conditions. If you're interested in the specifics, you can dig into the full research on the MEA industrial hose market from IMARC Group.
By taking the time to calculate your true pressure needs and accounting for the real-world effects of temperature, you’re not just buying a product off a spec sheet. You're building a system that's designed to handle the stress of the actual job site, protecting both your investment and your team.
Getting Installation and Maintenance Right
Picking the perfect hybrid hose and coupling is a great start, but it's really only half the job. If you want that setup to last and keep your operations safe, you absolutely have to get the installation right and stick to a solid maintenance plan. Even the best gear will fail if it's installed poorly or just left to fend for itself.
Think of it this way: installation is the foundation for the hose's entire life. A rushed job that leaves kinks or stress points is just asking for a blowout down the line. Spending a little extra time upfront to route it properly will save you from major headaches, costly downtime, and serious safety risks later.

The Golden Rules of Hose Installation
A proper installation all comes down to one thing: minimizing stress on the hose assembly. Every bend and point of contact is a potential failure waiting to happen if you don't manage it correctly.
I've seen it all, and these are the non-negotiable rules I follow on every job:
- Don't Let It Twist: A hose is made to bend, not to be twisted along its axis. I can't stress this enough. Twisting a hose during installation can slash its service life by as much as 70% and seriously weaken its pressure rating. If you need to accommodate rotation, use a swivel fitting.
- Mind the Bend Radius: Every hose has a minimum bend radius listed in its specs. Don't ignore it. Bending a hose tighter than it's designed for will create a kink, choking the flow and putting a permanent weak spot in the reinforcement. Always give your hoses plenty of room for wide, gradual curves.
- Guard Against Abrasion: Never let a hose rub against sharp edges, equipment, or even concrete flooring. That constant friction will chew through the outer cover in no time, exposing the reinforcement to moisture and damage. If you can't reroute it, use a protective sleeve.
Your Practical Maintenance Checklist
Once a hose is up and running, you can't just forget about it. A proactive maintenance schedule is your best defense against unexpected failures. This isn't just a quick look-over; it's a systematic inspection.
A documented maintenance routine shifts your team from being reactive to proactive. Instead of cleaning up a mess after a hose fails, you spot the warning signs early and schedule a replacement on your own terms.
Your routine visual checks should include:
- Cracks & Scuffs: Look closely at the outer cover for any signs of wear, especially in areas that flex or might rub against other surfaces.
- Leaks & Bubbles: Check for any dampness around the fittings or blisters forming under the cover. A bubble means the inner tube has a pinhole leak.
- Kinks & Damage: Make sure the hose hasn't been crushed or kinked. These spots become incredibly weak.
- Coupling Integrity: Inspect the couplings for corrosion or any sign they might be slipping off the hose. A compromised seal is a major red flag.
For more on building out a comprehensive inspection plan, our guide on the importance of preventive maintenance provides a great framework.
When to Call It Quits: Retiring a Hose
Every industrial hose has an expiration date. Knowing when to take a hose out of service is one of the most important safety skills your team can have. Never, ever try to patch up a worn-out hose, especially in a high-pressure system. The risk just isn't worth it.
Pull a hose from service immediately if you spot any of these:
- Exposed or broken reinforcement wires.
- Permanent kinks or crushed areas.
- Blisters, soft spots, or significant swelling.
- Any leak, no matter how small, from the hose or the coupling.
Proper installation and diligent maintenance are the keys to a safe and efficient operation. For systems carrying gas, it's also worth reviewing specific gas hose safety guidelines. By following these practices, you'll protect your people, prevent expensive failures, and get the reliable performance you paid for from your hybrid hoses & couplings.
Your Top Questions About Industrial Hoses Answered
Even the most seasoned engineers and project managers have questions when it comes to selecting the right components. When you're dealing with high-pressure systems, there's no room for guesswork. Here are some of the most common questions we get on the ground, with straight-up answers from our experience.
Is It Okay to Use a Hose with a Higher Pressure Rating Than I Need?
Not only is it okay, it’s actually a great idea. I’ve seen it save a lot of headaches down the line. Think of it as building in a safety cushion. If your system is prone to pressure spikes or water hammer, that extra capacity can be the difference between a normal workday and a costly failure.
For example, let's say your system operates at a steady 2,000 PSI. Grabbing a hose rated for 3,000 PSI isn't overkill; it's a smart, preventative measure. That hose is under less stress during everyday use, which almost always translates to a longer, more reliable service life.
How Often Do I Really Need to Inspect My Hoses?
This really boils down to how hard the hose is working. For your most critical or high-stress applications—think high-pressure lines, extreme heat, or hoses that are constantly being moved and flexed—a quick visual check every day is non-negotiable. For less demanding jobs, you can probably get away with a thorough inspection once a week or even once a month.
The most important thing is to have a routine and stick to it. Don't just leave it to memory. A documented schedule for checking for leaks, wear spots, kinks, or bubbles is your best defense against a sudden, dangerous blowout.
What’s the Real Difference Between a Hybrid Hose and a Regular Rubber One?
The magic is in the materials. A standard rubber hose is usually just that—rubber, like EPDM or nitrile. They’re tough, no doubt, but can also be heavy and stiff, especially when it gets cold.
A hybrid hose, however, is a blend of materials, usually a mix of PVC and rubber polymers. This combination gives you the best of both worlds, and the advantages are noticeable right away:
- Much Lighter: You'll often find they're up to 40% lighter than their all-rubber counterparts.
- More Flexible: They stay pliable and easy to handle, even on a cold morning.
- Tougher Than They Look: You get the abrasion resistance of modern polymers backed by the strength of rubber.
This is why selecting hybrid hoses and couplings is a fantastic move for any job that requires the hose to be dragged around or maneuvered frequently. You get the durability you need without the back-breaking weight.
At Yasu Trading Co. LLC, we stock the high-quality hoses, couplings, and industrial supplies that keep your operations running safely and efficiently. Dive into our extensive catalog to find the exact components your application demands. Get a quote from Yasu Trading Co. LLC today.